Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-02-15 Origin: Site








What keeps a gutter in place? It’s the small part most ignore. A Gutter Hanger holds the system steady. Poor quality can cause sagging and leaks.
In this article, you will learn why strength matters. We will explore durability, corrosion resistance, and performance.
A Gutter Hanger is more than a small fastening component—it is the primary structural link between the gutter channel and the fascia board. When quality is compromised, the entire roof drainage system becomes vulnerable to sagging, misalignment, and premature failure. High-quality hangers are engineered to withstand continuous load stress, seasonal expansion and contraction, and environmental exposure, all of which directly influence long-term durability. Inferior products, by contrast, often fail due to metal fatigue or insufficient structural thickness, creating hidden maintenance costs over time.
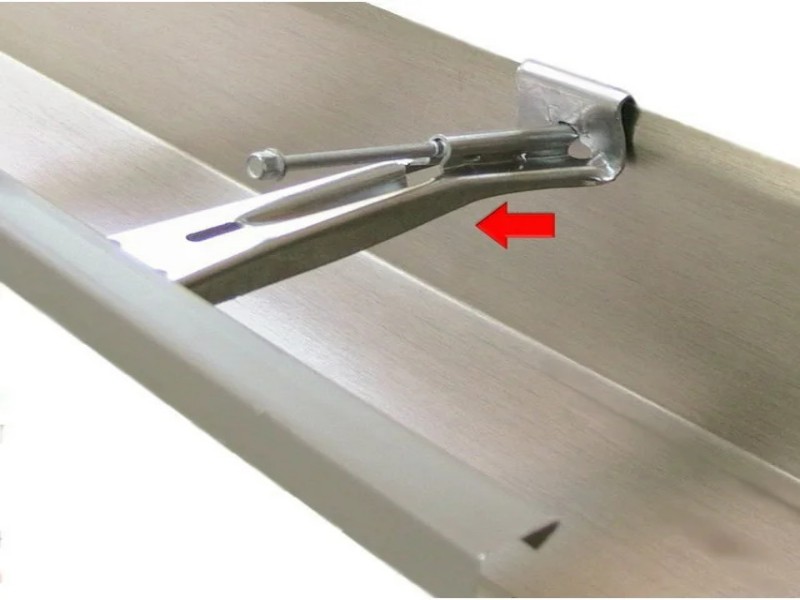
Structural integrity begins with material gauge and load-bearing design. A thicker, properly formed Gutter Hanger distributes water weight evenly along the gutter run, reducing localized stress points that lead to bending or cracking. Metal thickness is not merely about weight—it determines how well the hanger resists torsion during heavy rainfall or snow accumulation. When the bracket flexes under load, it weakens incrementally, eventually compromising alignment and drainage performance.
Below is a comparison of structural characteristics that influence durability:
Structural Factor | Low-Quality Gutter Hanger | High-Quality Gutter Hanger | Durability Impact |
Metal Gauge | Thin, lightweight | Thicker reinforced steel or aluminum | Resists bending under heavy load |
Bracket Design | Minimal reinforcement | Ribbed or formed support profile | Improved structural stability |
Fastening Strength | Standard screws | Corrosion-resistant heavy-duty fasteners | Prevents loosening over time |
Load Distribution | Uneven stress points | Even weight distribution | Reduces long-term fatigue |
Beyond thickness, design geometry plays a crucial role. Reinforced profiles or ribbed forms improve rigidity without adding excessive weight. This balance ensures that the Gutter Hanger can maintain structural stability while preserving gutter alignment, even in areas exposed to frequent storms or heavy snow loads.
While lower-grade hangers may appear economical at installation, they often generate cumulative expenses due to early replacement or fascia board damage. When structural weakness leads to sagging, water overflow may occur, increasing the risk of foundation erosion or siding deterioration. These secondary damages frequently cost far more than the initial savings achieved by selecting inexpensive hardware.
From a lifecycle perspective, durability directly affects return on investment. A high-quality Gutter Hanger typically extends system lifespan, reduces inspection frequency, and minimizes emergency repairs. Over 10–15 years, the savings in maintenance, labor, and replacement materials can significantly outweigh the slightly higher upfront cost. For property owners in regions with extreme weather conditions, durability is not simply a performance feature—it is a risk management strategy that safeguards the entire roof drainage infrastructure.
Corrosion remains one of the most common causes of Gutter Hanger failure. Because hangers are continuously exposed to moisture, temperature shifts, and sometimes salt-laden air, selecting the right material is critical. Material composition, coating technology, and environmental suitability collectively determine long-term corrosion resistance and overall performance.
Galvanized steel is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and protective zinc coating. The zinc layer acts as a sacrificial barrier, preventing rust from attacking the core steel. In moderate climates, galvanized Gutter Hangers provide reliable durability and sufficient structural strength for residential applications. However, in highly humid or coastal environments, zinc layers may degrade faster, requiring more frequent inspections.
The advantage of galvanized steel lies in its balance between affordability and mechanical strength. It offers strong load capacity, making it suitable for regions with heavy rainfall. When properly maintained, galvanized options can deliver stable long-term performance without excessive material costs.
Material selection often comes down to performance priorities. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, forming a passive protective layer that prevents oxidation. Aluminum, on the other hand, provides natural corrosion resistance and lighter weight, making it easier to handle during installation.
Material | Corrosion Resistance | Weight | Strength | Ideal Use Environment |
Stainless Steel | Excellent | Heavier | Very High | Coastal & high-humidity regions |
Aluminum | Good | Lightweight | Moderate | Residential, moderate climates |
Galvanized Steel | Moderate | Moderate | High | Standard rainfall areas |
Stainless steel Gutter Hangers are often recommended for coastal regions where salt exposure accelerates rust formation. Aluminum hangers are preferred when ease of installation and moderate corrosion resistance are sufficient. The decision should align with environmental exposure, structural requirements, and expected lifespan.
Beyond base materials, protective finishes significantly enhance corrosion resistance. Powder coatings, epoxy treatments, and polymer layers create an additional moisture barrier, reducing oxidation risk. These coatings also improve aesthetic consistency, especially in visible gutter systems.
Advanced surface treatments can extend service life by shielding the metal from UV degradation and chemical exposure. However, coating quality varies widely, and poorly applied finishes may chip or peel, exposing the underlying metal. For long-term durability, both material and coating performance must be evaluated together rather than independently.
Environmental exposure should guide every material decision. In high-humidity areas, continuous moisture increases the risk of electrochemical corrosion. Coastal regions introduce salt spray, which accelerates metal degradation and shortens product lifespan.
When selecting a Gutter Hanger for such environments, consider the following factors:
● High chromium stainless steel for maximum resistance
● Marine-grade coatings for added protection
● Fasteners made from matching corrosion-resistant alloys
● Increased inspection frequency for early detection of oxidation
Choosing corrosion-resistant materials is not simply a technical preference—it is essential for maintaining structural stability and ensuring consistent drainage performance. By aligning material properties with environmental conditions, property owners can significantly reduce failure risk and extend the overall service life of their gutter system.
A Gutter Hanger must support far more than just the visible gutter channel. It carries dynamic rainwater flow, seasonal snow accumulation, and occasional debris buildup. Structural stability depends on how well the hanger distributes this weight along the fascia board without creating stress concentration points. When load capacity is underestimated, the entire roof drainage system becomes vulnerable to sagging, misalignment, and long-term deformation.
Durability under load is therefore a combination of material strength, correct spacing, and fastening integrity. Even a high-grade metal hanger will fail prematurely if installed too far apart or exposed to excessive localized pressure.
Water weight increases rapidly during intense rainfall, especially when drainage slows due to debris. Snow and ice introduce prolonged static pressure that may exceed normal rainfall load by several multiples. These forces are not evenly distributed; instead, they accumulate in low points, creating structural imbalance.
Below is a simplified structural comparison of common load stresses:
Load Type | Nature of Force | Structural Risk to Gutter Hanger |
Heavy Rainfall | Dynamic moving weight | Gradual bending over time |
Standing Water | Static continuous load | Sagging between brackets |
Snow Accumulation | Long-duration pressure | Permanent deformation |
Ice Dams | Concentrated edge force | Fastener loosening |
Because snow and ice remain in place for extended periods, they are often more damaging than rain. High-quality Gutter Hangers are engineered with reinforced profiles to withstand this sustained downward pressure without losing alignment.
Spacing directly determines how effectively load is distributed. Wider intervals create longer unsupported spans, increasing bending force at the center of each section. Closer spacing reduces flex, stabilizes the gutter line, and improves overall drainage efficiency.
Key structural considerations include:
● Climate Exposure: Regions with heavy snowfall typically require reduced spacing to prevent sagging under seasonal load.
● Gutter Material Type: Lightweight aluminum systems may need tighter spacing compared to steel systems to maintain structural rigidity.
● Roof Pitch and Length: Longer horizontal runs amplify cumulative water weight, demanding consistent support intervals.
Correct spacing transforms individual brackets into a unified support framework. Instead of acting as isolated fasteners, the hangers function collectively to maintain consistent slope and structural stability.
Sagging rarely occurs suddenly; it develops gradually as repeated load cycles weaken structural integrity. Once alignment shifts, water begins to pool at low points, increasing stress on specific Gutter Hangers and accelerating corrosion risk.
Preventative stability relies on three integrated principles:
1. Adequate load-rated materials capable of resisting bending.
2. Proper installation spacing aligned with regional weather conditions.
3. Secure corrosion-resistant fasteners that maintain grip strength over time.
When these factors work together, the gutter system retains its intended slope, ensuring smooth water flow and minimizing overflow risk.
Structural strength alone does not determine longevity. Environmental exposure continuously challenges the material integrity of every Gutter Hanger. Moisture, temperature fluctuation, and UV radiation create cumulative stress that may not be visible initially but gradually reduces performance capacity.
Long-term durability depends on selecting materials that can tolerate repeated environmental cycles without structural fatigue.
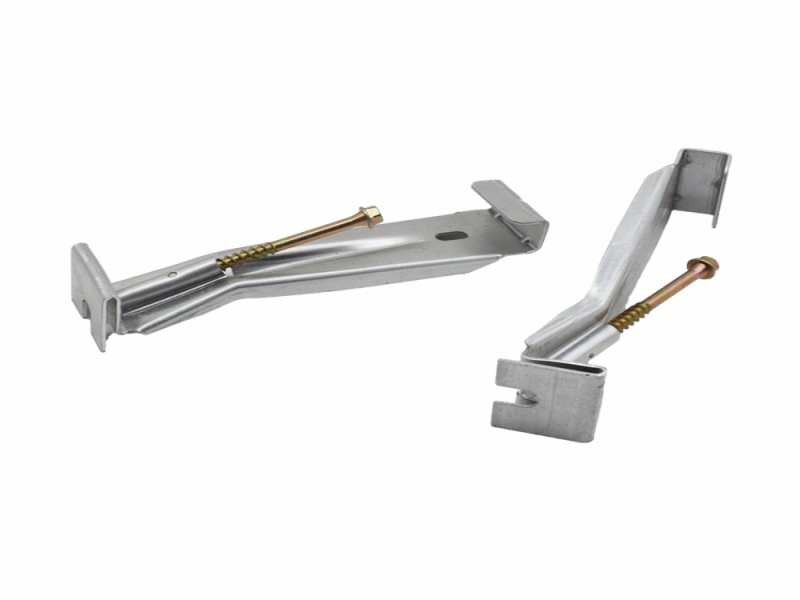

In colder climates, freeze–thaw cycles impose repeated expansion pressure on both the gutter and its supporting hangers. When trapped water freezes, it expands and exerts outward force. As temperatures rise and ice melts, the pressure is released—but microscopic structural strain remains.
Over time, this repeated stress contributes to metal fatigue. Weak points often develop near fastening holes or bends in the hanger bracket. Higher-grade alloys with superior tensile strength are better equipped to resist crack formation under cyclical stress.
Environmental fatigue risk increases when:
● Water drainage is partially obstructed
● Hangers are installed at excessive spacing
● Protective coatings are compromised
Addressing these vulnerabilities early reduces long-term structural degradation.
Metal expands in heat and contracts in cold weather. Although these dimensional changes are small, repeated cycles introduce stress at fastening points. If expansion tolerance is not accounted for, screws may loosen, and structural alignment may shift.
To manage expansion-related stress effectively, consider the following performance factors:
● Material Compatibility: Using similar metals for both gutter and hanger minimizes differential expansion.
● Flexible Fastening Design: Allows slight movement without compromising structural grip.
● Surface Protection: Reduces corrosion that could amplify stress at connection points.
By selecting climate-appropriate materials and maintaining proper installation standards, a Gutter Hanger system can sustain consistent structural performance across multiple seasons.
Even the highest-grade Gutter Hanger cannot deliver optimal performance if installation practices are inconsistent or structurally flawed. Installation determines how load is distributed across the fascia, how effectively slope is maintained for drainage, and how well the system resists long-term environmental stress. A precisely installed hanger system works as an integrated structural network, while poor alignment or uneven spacing transforms individual brackets into isolated stress points that compromise durability.
Installation quality affects three core performance dimensions simultaneously: structural stability, drainage efficiency, and long-term maintenance requirements. If the initial slope is incorrect or fastening depth is insufficient, the system may begin to fail gradually under seasonal load. These issues often remain invisible until sagging or overflow becomes noticeable, at which point structural correction becomes more costly and labor-intensive.
From a performance standpoint, proper installation involves more than attaching brackets at equal intervals. It requires careful consideration of fascia board integrity, correct fastener selection, and alignment verification before the first rainfall event. When these variables are carefully managed, the Gutter Hanger system supports consistent water flow and resists premature mechanical fatigue.
Critical Installation Factors Influencing Performance
Installation Variable | Structural Effect | Long-Term Impact |
Correct Spacing | Even load distribution | Prevents sagging between brackets |
Secure Fastening Depth | Strong fascia anchoring | Reduces loosening over time |
Proper Slope Alignment | Efficient drainage flow | Minimizes standing water stress |
Fascia Board Condition | Stable mounting base | Prevents structural shifting |
Installation should always be evaluated in relation to environmental exposure. Regions with heavy snow or intense rainfall may require closer spacing and reinforced fastening methods. By aligning installation standards with regional climate demands, property owners can significantly extend the operational lifespan of the entire roof drainage system.
Failure of a Gutter Hanger rarely results from a single factor. Instead, it is typically the cumulative effect of corrosion, mechanical stress, improper installation, and environmental exposure. Understanding the root causes of failure allows for targeted prevention strategies that protect both structural stability and drainage performance.
Early warning signs often include slight gutter misalignment, visible rust spots, or minor fastener movement. While these indicators may seem minor, they often signal deeper structural compromise developing beneath the surface. Proactive inspection and maintenance are therefore essential components of long-term system reliability.
Corrosion gradually reduces the structural thickness of metal components, weakening their ability to withstand load pressure. In humid or coastal environments, moisture exposure accelerates oxidation, particularly at connection points where protective coatings may wear down. Once corrosion penetrates the surface layer, the metal’s load-bearing capacity decreases, increasing the risk of bending or fracture.
Structural weakening due to corrosion often follows this progression:
1. Surface oxidation begins at exposed edges or fastener holes.
2. Protective coating deteriorates, exposing base metal.
3. Metal cross-section thins, reducing tensile strength.
4. Load pressure triggers bending or cracking.
Preventative strategies should focus on material selection and periodic inspection. Using corrosion-resistant alloys, maintaining intact protective coatings, and replacing compromised fasteners early can significantly delay structural degradation. In high-risk environments, scheduled inspections after seasonal weather extremes are particularly beneficial.
Fasteners serve as the critical anchor point between the Gutter Hanger and the fascia board. When screws loosen due to vibration, expansion cycles, or wood deterioration, structural stability declines rapidly. A single loosened fastener may shift load distribution to adjacent brackets, increasing stress concentration and accelerating system imbalance.
Fascia board condition also plays a crucial role. Wood rot, moisture infiltration, or structural cracking weakens the mounting surface, reducing anchoring strength even if the hanger itself remains intact. Over time, repeated stress cycles may enlarge fastener holes, making re-tightening ineffective without structural reinforcement.
To prevent fastener-related failures, consider the following measures:
● Use corrosion-resistant screws compatible with the hanger material to reduce galvanic reaction.
● Inspect fascia boards for signs of moisture damage before installation or replacement.
● Re-secure or replace loosened fasteners promptly to maintain even load distribution.
By combining secure fastening techniques with regular structural evaluation, property owners can prevent minor mechanical issues from escalating into full system failure. Proper maintenance, paired with high-quality materials and precise installation, ensures that the Gutter Hanger continues to provide reliable structural support and consistent drainage performance over time.
High-quality gutter hangers support system strength and stability. They resist corrosion and heavy weather stress. Proper spacing and installation improve long-term performance.Strong materials reduce sagging and costly repairs. Durable coatings protect against rust and fatigue. Smart design keeps drainage smooth and reliable.Hangzhou Wonder Hardware Manufacturing Co., Ltd. offers precision-engineered gutter hanger solutions. Their products deliver strength, corrosion resistance, and lasting value.
A: A high-grade Gutter Hanger resists bending and metal fatigue, maintaining structural stability under sustained water and snow loads.
A: Corrosion reduces the cross-sectional strength of a Gutter Hanger, weakening load capacity and increasing the risk of failure.
A: Proper Gutter Hanger spacing depends on climate and load requirements, typically closer in heavy snow regions to prevent sagging.
A: Incorrect alignment or fastening can overload each Gutter Hanger, affecting drainage efficiency and long-term structural integrity.