Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-02-14 Origin: Site








Why do gutters fail early? Often, support is the cause.A strong Gutter Hanger keeps water flowing safely. It protects roof edges and fascia boards.Roofing and villa needs differ. Load and design both matter.In this article, you will learn how to compare options and choose wisely.
An Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hanger is a structural support component designed specifically to secure K-style gutters along the fascia board of a roofing system. Unlike spike-and-ferrule systems, a modern Gutter Hanger provides concealed internal support, distributing weight evenly across the gutter body while maintaining structural alignment. Because K-style gutters feature a flat back and decorative front profile, the hanger must not only anchor securely but also preserve slope precision to ensure efficient rainwater drainage. In roofing and villa applications, the reliability of the entire roof drainage system depends heavily on how effectively the Gutter Hanger manages load transfer and alignment stability.
In practical terms, the hanger functions as both a fastening mechanism and a structural reinforcement point. It connects the gutter to the fascia while resisting deformation from water accumulation, wind uplift, and seasonal expansion or contraction. Choosing aluminum alloy as the base material enhances performance without adding unnecessary weight to the roof edge, making it particularly suitable for residential and light commercial projects.
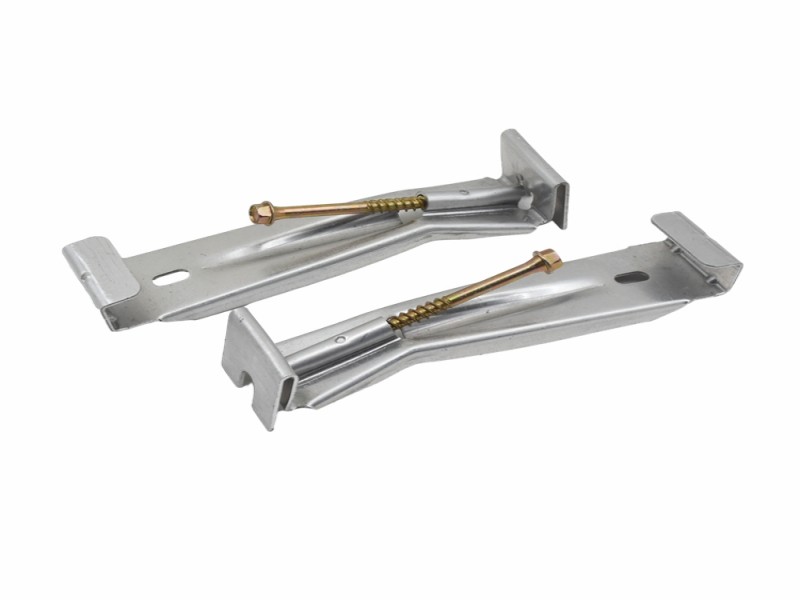

The structural purpose of a Gutter Hanger goes beyond simple attachment. It acts as a load-bearing intermediary between the gutter channel and the building structure. Because rainwater flows through the gutter with continuous directional force, maintaining a consistent slope (typically around 1/4 inch per 10 feet) is essential. Even minor misalignment can cause water pooling, overflow, or fascia damage over time.
Key structural functions include:
● Maintaining gutter alignment and slope:
A properly spaced Gutter Hanger ensures the gutter remains straight along the roofline, preserving its pitch toward the downspout. When alignment is maintained, water flows efficiently without stagnation or backflow. Over long spans, evenly distributed hangers prevent gradual tilt caused by uneven fastening.
● Preventing sagging under water load:
During heavy rainfall or snow melt, gutters experience significant downward force. Aluminum alloy hangers distribute this weight across multiple anchor points, reducing localized stress. Without adequate structural support, the gutter may bow outward, leading to seam separation or joint leakage.Below is a simplified comparison of structural behavior under load:
Structural Aspect | Properly Installed Gutter Hanger | Insufficient or Weak Support |
Load Distribution | Evenly spread along fascia | Concentrated at limited points |
Slope Retention | Maintains designed pitch | Gradual misalignment |
Resistance to Sagging | High structural stability | Visible gutter bowing |
Long-Term Integrity | Reduced joint stress | Increased risk of leakage |
The performance difference becomes especially noticeable in larger roofing systems where drainage volume increases. In villa applications, aesthetic alignment is equally critical, meaning sagging or misalignment not only affects function but also architectural appearance.
The choice of aluminum alloy for a Gutter Hanger directly influences durability, handling, and long-term reliability. Compared to steel or plastic alternatives, aluminum alloy offers a balanced combination of mechanical strength and environmental resistance, making it highly suitable for exterior installation.
Aluminum alloy provides impressive structural rigidity without excessive mass. Because roof edges and fascia boards should not bear unnecessary additional weight, using lightweight support hardware minimizes strain on the building envelope. Despite being lighter than steel, aluminum maintains sufficient tensile strength to resist bending and pull-out forces under heavy rain or snow conditions.
Exterior drainage systems are continuously exposed to moisture, UV radiation, and airborne contaminants. Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that resists corrosion, significantly extending service life in humid or coastal environments. When paired with compatible fasteners, aluminum alloy hangers reduce the risk of galvanic corrosion, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Temperature fluctuations cause materials to expand and contract. Aluminum alloy demonstrates predictable thermal behavior, allowing it to maintain structural form without cracking or warping. This dimensional stability is essential for preserving gutter alignment across seasonal cycles. In villa projects where architectural consistency matters, stable hanger geometry prevents visible distortion along the roofline.
Material Performance Overview
● Lightweight yet structurally strong
● Naturally corrosion-resistant
● Suitable for long-term outdoor exposure
● Compatible with common fascia materials
● Stable under thermal expansion cycles
When comparing Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hangers, performance differences often become evident only after installation—when the system faces real environmental stress. A well-informed comparison should focus on structural strength, corrosion resistance, design configuration, and installation compatibility. Each of these factors influences long-term durability, visual outcome, and maintenance requirements in both roofing and villa applications.
Structural integrity is the foundation of any effective Gutter Hanger system. Since K-style gutters typically carry significant volumes of rainwater, especially during storms or rapid snow melt, the hanger must resist both vertical load and outward pull forces. The combination of material thickness, rib reinforcement, and screw anchoring depth determines whether the hanger can maintain its form under stress.
Resistance to bending and pull-out
Bending resistance depends on alloy grade, cross-sectional design, and reinforcement geometry. A well-designed hanger distributes weight evenly along its body, preventing concentrated stress at the screw point. Pull-out resistance, on the other hand, relates to screw engagement depth and fascia board integrity. If anchoring is shallow or poorly aligned, even a strong aluminum bracket can fail prematurely.Performance under heavy rain or snow
Extreme weather increases both static and dynamic loads. During prolonged rainfall, water accumulation increases sustained downward pressure, while snow and ice add additional weight that can exceed standard design loads. In colder regions, freeze-thaw cycles intensify stress as ice expansion pushes against gutter walls. Therefore, spacing recommendations and hanger thickness must align with climate conditions.Below is a structural comparison overview:
Performance Factor | Standard-Duty Hanger | Heavy-Duty Reinforced Hanger |
Typical Load Rating | Moderate rainfall areas | High rainfall / snow regions |
Rib Reinforcement | Basic structural form | Enhanced rib or bracket design |
Pull-Out Resistance | Dependent on fascia strength | Higher screw engagement capacity |
Sag Prevention | Suitable for short spans | Suitable for wide roof spans |
Choosing the appropriate load capacity prevents sagging, joint separation, and long-term structural fatigue.
Because Gutter Hangers operate in permanently exposed outdoor conditions, environmental resistance is critical. Aluminum alloy offers natural oxidation protection through the formation of a passive oxide layer. This protective layer shields the metal from progressive corrosion, especially in areas with frequent rainfall.
Oxidation resistance
Unlike untreated steel, aluminum does not rust in the traditional sense. Instead, it forms a thin protective coating that slows further chemical reaction. Surface treatments such as powder coating or anodizing can further enhance durability. These treatments reduce surface pitting and preserve appearance in visible residential installations.Suitability for humid or coastal regions
In coastal areas, salt-laden air accelerates corrosion in many metals. Aluminum alloy, particularly marine-grade variations, performs significantly better than untreated ferrous materials. However, compatibility between hanger material and fastening screws remains essential to avoid galvanic corrosion. Stainless steel or coated screws are often recommended to maintain system integrity.Environmental exposure considerations typically include:
● Moisture intensity and frequency
● Salt exposure levels
● UV radiation impact
● Temperature fluctuation range
A hanger’s environmental performance determines whether it maintains both structural reliability and aesthetic consistency over decades of exposure.
Design configuration affects not only structural performance but also architectural presentation. Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hangers are generally available in hidden (internal) or exposed (external bracket) formats. Each type has practical advantages depending on application context.
Hidden hangers are installed inside the gutter channel, making them invisible from ground level. This design enhances visual integration, particularly in villas or high-end residential buildings where exterior lines must remain clean and uninterrupted. The concealed system also distributes weight across the inner gutter wall, improving load stability.
Exposed support brackets, by contrast, remain visible along the outer gutter edge. While they may not offer the same seamless aesthetic, they often provide additional reinforcement in heavy-load scenarios. In large roofing systems or commercial structures, exposed brackets may offer easier inspection and maintenance access.
Design comparison summary:
● Hidden support: Prioritizes appearance, suitable for residential settings, streamlined visual profile.
● Exposed support: Prioritizes accessibility and reinforcement, often used in functional roofing applications.
Structural trade-offs should be evaluated alongside aesthetic requirements to determine the most appropriate configuration.
Even the strongest Gutter Hanger will underperform if installation compatibility is overlooked. Proper fascia attachment, screw selection, and alignment accuracy directly influence structural lifespan.
Fascia attachment considerations
The hanger must be secured into solid fascia material capable of supporting dynamic loads. Wood fascia boards require corrosion-resistant screws with adequate penetration depth. Metal fascia systems may require self-drilling fasteners designed to prevent slippage. The angle and spacing of attachment points must align with the intended gutter pitch to ensure consistent drainage.Screw type compatibility
Fasteners should match both the hanger material and environmental conditions. Stainless steel screws reduce corrosion risk, while coated carbon steel screws offer cost-effective durability in moderate climates. Improper screw choice can lead to premature weakening at the anchor point.Installation efficiency
Ease of installation impacts labor time and alignment precision. Modern aluminum hangers often integrate pre-drilled holes or snap-in designs that simplify positioning. Reduced installation complexity improves consistency across long roof spans, lowering the likelihood of slope deviation.When comparing installation factors, consider:
● Fascia material type
● Required screw penetration depth
● Climate-related corrosion risk
● Spacing consistency across the roofline
A well-matched installation system ensures that the Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hanger performs as intended, maintaining structural strength, resisting environmental stress, and preserving architectural integrity throughout its service life.
Selecting the right Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hanger requires understanding how structural priorities shift between large-scale roofing systems and residential villa applications. While the core function of a Gutter Hanger remains consistent—supporting the gutter and maintaining drainage slope—the environmental stress level, architectural expectations, and installation scale differ significantly. Evaluating these contextual differences ensures that structural capacity, design configuration, and long-term reliability align with the specific building type.
Roofing systems, especially those covering multi-unit buildings or extended rooflines, place higher mechanical demands on each Gutter Hanger. Because drainage volume increases proportionally with roof surface area, hangers must withstand greater sustained loads during heavy rainfall. In colder climates, accumulated snow and ice further amplify downward pressure, making load capacity a primary selection factor.
Larger drainage volumes
In large roofing systems, gutters may channel water from expansive slopes into a limited number of downspouts. This concentration increases hydrostatic force inside the gutter channel. If hanger spacing is too wide or reinforcement insufficient, sagging may occur. Reinforced aluminum alloy hangers with deeper rib structures are typically recommended for such scenarios.Wider spacing challenges
Although wider hanger spacing may reduce installation time and material cost, it increases structural stress between anchor points. Over long spans, even slight miscalculations can lead to slope deviation. Therefore, structural analysis should consider roof pitch, rainfall intensity, and fascia board strength before finalizing spacing intervals.Structural priority over aesthetics
In commercial or industrial roofing systems, performance reliability generally outweighs visual considerations. Exposed heavy-duty hangers may be preferred when additional reinforcement or easier inspection access is required. The emphasis is on maximizing load resistance and minimizing maintenance frequency rather than preserving architectural minimalism.
Villa projects introduce a different set of priorities where structural reliability must coexist with architectural refinement. While the functional demands of drainage remain important, visual harmony and concealed installation often take precedence in residential design.
Architectural appearance
In high-end residential properties, the roofline contributes significantly to overall curb appeal. Visible hardware can disrupt clean exterior lines. Therefore, hidden Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hangers are frequently selected to maintain seamless integration with decorative K-style gutter profiles.Concealed hanger preference
Hidden support systems are installed within the gutter channel, remaining invisible from ground level. This configuration not only enhances aesthetic continuity but also distributes weight evenly along the inner wall of the gutter. However, installers must ensure precise alignment to avoid internal stress accumulation.Balanced strength and visual harmony
Although villas may not always face the same extreme loads as commercial roofing systems, durability remains essential. The selected hanger must still provide adequate resistance to bending and environmental exposure. The goal is to achieve a balance between structural reliability and architectural elegance without compromising either aspect.
To simplify selection, the following framework compares key considerations across application types:
Decision Factor | Roofing Systems | Villa Projects |
Primary Priority | Load capacity and durability | Visual integration and balance |
Typical Hanger Type | Heavy-duty or reinforced | Hidden internal support |
Spacing Strategy | Closer spacing in heavy-load regions | Standard spacing with alignment focus |
Inspection Needs | Accessibility for maintenance | Minimal visible hardware |
When to choose heavy-duty models:
If the building experiences high rainfall, snow loads, or extended roof spans, reinforced aluminum hangers with closer spacing are recommended. These models reduce the risk of sagging and structural fatigue over time. Heavy-duty designs are especially appropriate for commercial facilities and large residential complexes.When to prioritize hidden design:
For villas and architecturally refined homes, concealed hangers maintain aesthetic continuity. Provided the load conditions remain within standard residential thresholds, hidden aluminum alloy hangers offer both sufficient strength and visual discretion.Key differentiators at a glance:
The decision ultimately depends on environmental stress levels, structural load expectations, and design intent. Aligning these factors ensures that the Gutter Hanger system performs reliably while complementing the building’s overall design language.
After determining application type, proper specification ensures long-term performance. Even the most durable Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hanger can underperform if spacing, compatibility, or installation planning is overlooked. A systematic approach minimizes installation errors and structural inconsistencies.
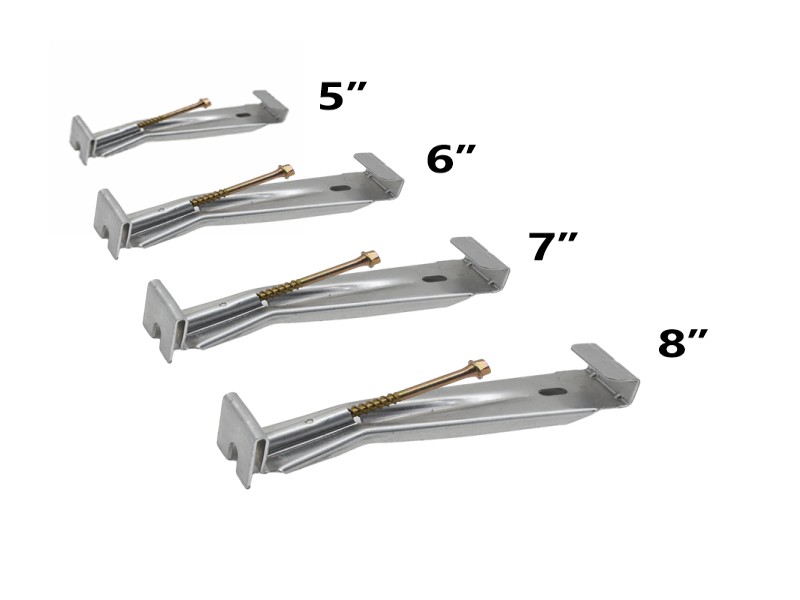
Spacing directly affects load distribution and slope stability. Standard residential installations often follow consistent intervals to maintain even weight transfer along the fascia. However, environmental conditions may require adjustments.
Standard spacing
For typical residential applications, hangers are commonly spaced at regular intervals to maintain alignment and prevent mid-span deflection. This ensures consistent slope toward the downspout and reduces water pooling risk.Adjustments for heavy-load roofs
In regions with heavy rainfall or snow accumulation, spacing intervals should be reduced to increase support density. Closer spacing distributes weight more evenly, minimizing stress concentration and extending system lifespan. Installers should evaluate local climate data when determining optimal intervals.Spacing considerations generally include:
● Roof surface area
● Expected precipitation intensity
● Gutter material thickness
● Fascia board strength
Proper spacing is a preventive strategy against long-term deformation.
Correct dimensional compatibility between the Gutter Hanger and K-style gutter profile is essential for structural integrity. Mismatched sizes can lead to instability, misalignment, and premature joint failure.
Matching hanger with K-style gutter dimensions
Hangers must correspond precisely to the gutter’s width and shape. An undersized bracket may fail to secure the gutter wall, while an oversized hanger may introduce lateral movement. Manufacturers typically specify compatibility ranges to ensure secure engagement.Avoiding fit instability
Improper fit increases vibration during wind events and weakens slope consistency. Over time, repeated movement can loosen fasteners and compromise fascia attachment. Verifying dimensional alignment before installation reduces long-term maintenance issues.Compatibility assessment should include:
● Gutter width measurement
● Profile depth verification
● Screw alignment positioning
● Fascia board thickness evaluation
Precision at this stage prevents performance issues later.
Before finalizing installation, reviewing a structured checklist ensures all performance variables are addressed:
Load requirement:
Assess expected rainfall volume, potential snow accumulation, and roof span length. Confirm that hanger load rating exceeds projected maximum stress.Climate exposure:
Evaluate humidity levels, coastal salt exposure, and temperature variation. Select aluminum alloy grade and compatible fasteners accordingly.Fascia structure:
Inspect fascia board material and condition. Ensure sufficient structural strength for screw anchoring and load transfer.Installation condition:
Verify slope alignment tools, spacing accuracy, and fastening torque consistency. Uniform installation technique directly influences long-term performance.By systematically evaluating these specification elements, project planners can ensure that the selected Aluminum Alloy K-Style Gutter Hanger delivers reliable structural support, maintains architectural alignment, and withstands environmental stress for years to come.
This article compares aluminum alloy K-style gutter hangers for roofing and villa projects. It focuses on strength, corrosion resistance, design types, and spacing choices.
Roofing systems often need higher load support and tighter spacing to prevent sagging. Villa projects usually prefer hidden support with a cleaner look and balanced strength.
Choosing the right Gutter Hanger improves long-term drainage reliability and protects the fascia line. Hangzhou Wonder Hardware Manufacturing Co., Ltd. offers durable hanger solutions with strong support and corrosion resistance, helping projects stay stable for years.
A: Select a Gutter Hanger with reinforced ribs and reduced spacing to handle higher rain or snow loads.
A: Standard spacing works for typical roofs, but closer intervals improve Gutter Hanger stability in high-precipitation areas.
A: A hidden Gutter Hanger offers cleaner aesthetics while maintaining structural support for residential projects.
A: Properly treated aluminum alloy helps the Gutter Hanger resist oxidation in humid or coastal environments.